Archive : Article / Volume 2, Issue 2
- Research Article | DOI:
- https://doi.org/10.58489/2836-5127/012
Development of Android-Based Multimedia Learning Media in Recognition 0f Human Body Anatomy (SI-MANTAN)
1,2,3,4 Universitas Hang Tuah Pekanbaru, Mustafa Sari Street No 5, Pekanbaru and 28288, Indonesia
Siska Mayang Sari
Rian Ordila, Asep Marzuki, Siska Mayang Sari, Rani Lisa Indra. Development of Android-Based Multimedia Learning Media in Recognition 0f Human Body Anatomy (SI-MANTAN). Journal of Radiology Research and Diagnostic Imaging.2(2) DOI:10.58489/2836-5127/012
© 2023 Siska Mayang Sari, this is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- Received Date: 23-02-2023
- Accepted Date: 20-03-2023
- Published Date: 31-03-2023
Android, Anatomy, Multimedia, Health, Learning Media
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic in the world since the beginning of 2020 until now is still a challenge for every as pect of life, including the world of education in the health sector. The use of technology is the main choice in the education system which is falsified in learning methods. There are many alternative learning methods by utilizing technology, one of which is multimedia-based learning. The use of multimedia today is more in demand than other methods. Health students have the opportunity to take advantage of the use of multimedia in the learning process to achieve competence while participating in learning in each course. One of the basic course study materials studied by health students is generally about the anatomy and physiology of the human body. Students experience obstacles in understanding the anatomy and physiology of the human body during the COVID-19 pandemic due to limited access to the laboratory as usual before the pandemic occurred.
Introduction
Early in 2020, a new type of coronavirus (SARS- CoV-2) or the disease called Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) quickly became a global pandemic. The number of spread and death due to this disease is quite high, so WHO states that this condition is a global emergency, an important agenda for all countries. This condition caused the government through the Ministry of Education and Culture (KEMENDIKBUD) to issue a circular dated March 17, 2020, regarding the learning process from home/distance learning as a form of preventing COVID-19.
Responding to the circular letter, every educational institution is required to optimize the use of technology in the learning process. The College of Health Sciences (STIKes) is one form of educational institution that must be able to apply learning methods based on the use of technology. Health student competencies are generally achieved during classroom learning, practice in hospitals, and laboratory skills on campus, one of which is the anatomy and physiology of the human body, where humans are the main clients. Students experienced difficulties in understanding the anatomy and physiology of the human body during the COVID- 19 pandemic due to limited access to the laboratory as usual before the pandemic occurred. There are many alternative learning methods in PJJ by utilizing technology, one of which is multimedia-based learning. The use of multimedia is currently more in demand than other methods because it is able to describe the material presented (2). Currently, there are many learning media applications that can be accessed freely by students, but very few are equipped with explanations and adapt to the learning competencies of their education level.
This study aims to develop multimedia-based learning media in increasing student competence in the introduction of human anatomy.
RESEARCH METHOD
The method that the author uses is the waterfall method. Broadly speaking, the waterfall method has the following steps: analysis, design, writing, testing and implementation and maintenance (Pressman, 2010).
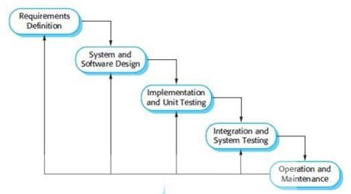
The following are the stages of the development of the Waterfall Development Model:
Software requirements analysis
In this process, the writer builds an android-based application. One alternative to help learning is to use an android smartphone which is currently growing rapidly. The android-based learning system is designed by applying interactive 3D so that it is very varied and interesting. This application has 3 main menus, namely Explanation of Body Anatomy, interactive 3D Anatomy of the Body and Multiple-Choice Quiz with existing materials and content to support learning for users who use it.
System design
In this Body Anatomy Learning Application Design process, the researcher uses Eclipse in making the program.
Coding
Coding is the process of translating the design into a form that can be understood by the machine, using a programming language. After all the designs are made, then an Android-based application is created. Making this program using Java applications and the eclipse editor.
Test
After the coding process is complete, it is continued with the testing process on the program. And check whether the results of the development are in accordance with the desired results.
Program Implementation
The program's implementation is the stage where the application is ready to operate in a state that is actually in accordance with early childhood education, so hat it will be known that the application made can produce the goals to be achieved.
Analysis and Design
In analyzing the system, a complete information system can be decomposed into component parts that aim to identify and evaluate problems so that they are determined to determine the weaknesses, opportunities and obstacles that occur as well as the expected needs so that they are implemented according to with expectations.
Problem analysis
The problem that must be discussed is the placement and terms and descriptions of body anatomy data obtained from various sources.
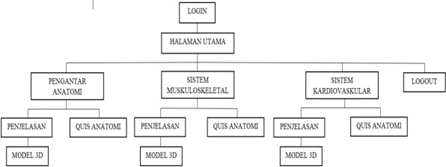
Si-Former Program Hierarchy
The following is the program hierarchy for the Si- Former application login page for users.
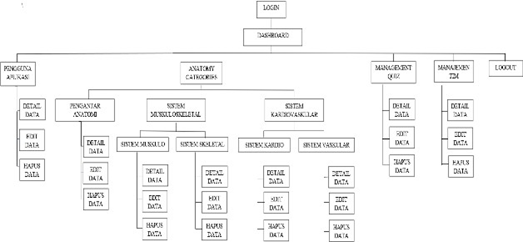
Administrator Si-Mantan ProgramHierarchy
The following is the program hierarchy for the Si- Former application login page for users.
RESULT
Theresults of the SI-MANTAN design are implemented using the PHP programming language:
Login page
The login page functions for Lecturers and Students to gain access to enter the system. Users are requiredto fill in the usernameand password that have been registered in the database.

Account Registration Page
This page serves for Lecturers and Students to register personal data, be it NIM, Full Name, College, Study Program, Email, Password as a Si-Former account submission to gain access to enter the system.

Dashboard Page
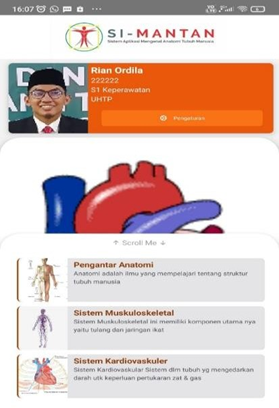
The Home Page (Dashboard) is the view that appears after the user logs into the application. Where you can directly choose what Anatomy Section you want to study.The results of the main menu display can be seen in the image below.
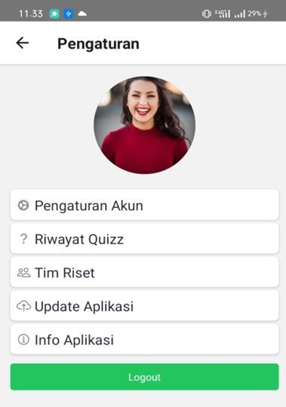
Setting page
This page serves to update Account Data, Quiz History Results that have been undertaken, Research Team Profiles, Application Updates and Application Info
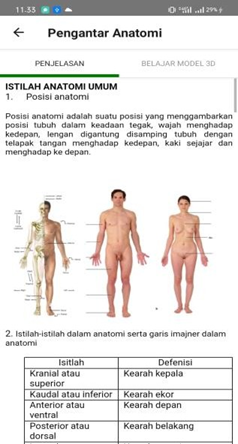
Anatomy Explanation Page
Anatomy Learning Pages with Narrative and Image
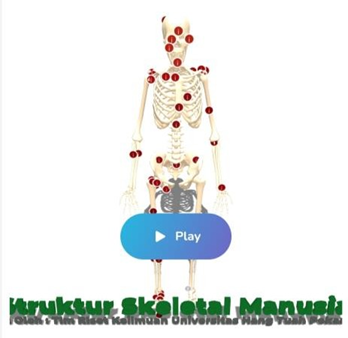
Interactive 3D Anatomy Learning Page where students can find out parts, Latin names, positions and brief explanations.


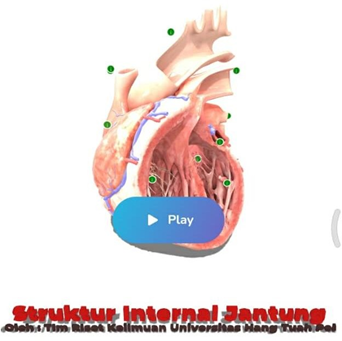
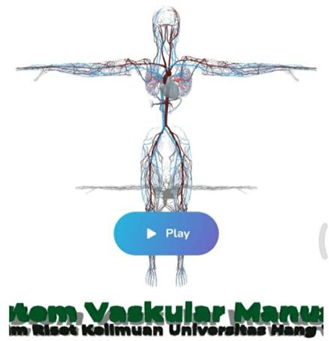
7.Quiz page
Quiz page where students can test their ability in understanding the material that has been given.

8. Quiz History Results Page
Anatomy Learning Pages in 3D Interactive where students can find out parts, Latin names, positions and brief explanations.
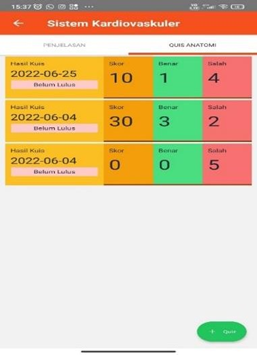
DISCUSSION
The application of interactive 3D using assembler is sufficient and capable of dis-playing human anatomy images / images stably for novice users, where in appearance the placement of the location of the information is quite detailed in providing information on every part of the human body anatomy.
Conclusion
From the discussion that can be described, the author tries to make conclusions and suggestions asfollows:
- With the SI-Mantan application, it will providea new experience in learning body anatomy.
- With the SI-Mantan, Health Students and Lecturers will have more convenience and efficiency in doing learning in the introduction of the Anatomy of the Human Body.
Acknowledgment
The author would like to thank the Universit as Hang Tuah Pekanbaru & Universit as Awal Bros Pekanbaru for being willing to provide support in conducting this re-search.
References
The template will number citations consecutively within brackets [1]. The sentence punctuation follows the bracket [2]. Refer simply to the reference number, as in [3]—do not use “Ref. [3]” or “reference [3]” except at the beginning of a sentence: “Reference [3] was the first . . .”
Number footnotes separately in superscripts. Place the actual footnote at the bottom of the column in which it was cited. Do not put footnotes in the reference list. Use letters for table footnotes.
Unless there are six authors or more give all authors' names; do not use “et al.”. Papers that have not been published, even if they have been submitted for publication, should be cited as “unpublished” [4]. Papers that have been accepted for publication should be cited as “in press” [5]. Capitalize only the first word in a paper title, except for proper nouns and element symbols.
For papers published in translation journals, please give the English citation first, followed by the original foreign-language citation[6].
References
- Bunafit Nugroho. (2008), Aplikasi Pemrograman Web Dinamis Dengan PHP dan MySQL, Gava Media,Yogyakarta.
- http://jurnal.stikes-aisyiyah-palembang.ac.id/index.php/JAM/article/view/572
- Jogiyanto, HM. (2001). Sistem teknologi informasi. Yogyakarta: Andi Cipta.
- Kadir, A. (2008). Belajar database menggunakan mysql.Yogyakarta: Andi
- Rini Agustina, S.Kom, M.Pd (2012) Pemrograman Aplikasi Android
- Pressman, R. S. (2010), Software Engineering: a practitioner's approach, McGraw-Hill, New York
- https://gk.jurnalpoltekkesjayapura.com/gk/article/view/139
- Sutabri, T. (2003). Analisa sistem informasi.Yogyakarta: Andi
- https://www.neliti.com/publications/468560/the-effect-of-cardiopulmonary-resuscitation-cpr-multimedia-learning-methods-on-h


